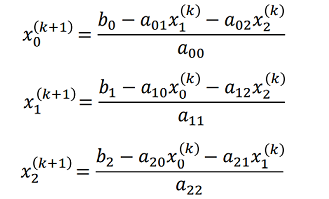 左記は、3元の場合でヤコビ法による計算手順で初期値としてXnにゼロ与えて、反復解法を行う計算式です。
左記は、3元の場合でヤコビ法による計算手順で初期値としてXnにゼロ与えて、反復解法を行う計算式です。但し、正解に近づくためには条件があります。
連立一次方程式の解法10
連立一次方程式の解法の続きで、今回は、線形システムの反復解法です。
ヤコビ法、ガウス・ザイデル法のプログラム例です、この計算方法についての詳細は、webで検索すれば、沢山検索出来ますのでそちらを参照して下さい。
反復計算で、解に収束するには、条件があるので実際の連立方程式の計算にはあまり使用されないようです。
ヤコビ法
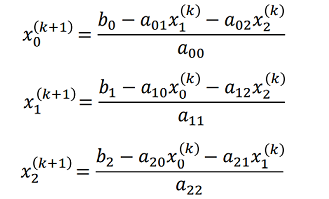 左記は、3元の場合でヤコビ法による計算手順で初期値としてXnにゼロ与えて、反復解法を行う計算式です。
左記は、3元の場合でヤコビ法による計算手順で初期値としてXnにゼロ与えて、反復解法を行う計算式です。
但し、正解に近づくためには条件があります。
ガウス・ザイデル法
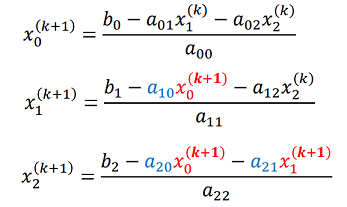 ヤコビ法を改良したものでガウス・ザイデル法です。
ヤコビ法を改良したものでガウス・ザイデル法です。
ヤコビ法より、速く収束します。
正解に近づくためには条件が存在しますが条件はヤコビ法よりは、かなり緩くなります。
収束条件
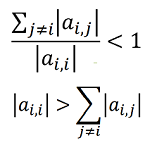 収束する条件は、各行の非対角の絶対値の和より対角の絶対値が大きいことです。
収束する条件は、各行の非対角の絶対値の和より対角の絶対値が大きいことです。
必ず収束するのは、全ての行が対角の絶対値が大きいことですが、一か所の行が条件を満たしていると、収束をする場合があります。
ガウス・ザイデル法の場合、最終行が条件を満たしている場合、他の行が条件を満たしていなくても、絶対値の比が 1 に近いほど収束する確率が高くなります。
当然最終行は絶対値の比が 1 より大きくなるのですが、この値が大きい程他の行の値は小さくても良くなります。
大きいのが最終行で無くても、収束しますが、1行目については、大きくしても効果は余りありません。
条件を満たすようにする為には、行の移動、列の移動を行います。
1行しか条件を満たしていない場合、現在は収束するかどうか解りません。
特に、解けない値なのか、収束しないだけなのか判別出来ないのが大きな問題です。
しかし、単純な計算の繰り返しなので、何らかの判別方法があると思われますが、つきとめている人はいない様です。
必ず解を求めることが出来る、LU分解や、消去法があるので、反復法でも計算が出来ると言う事なのでしょう。
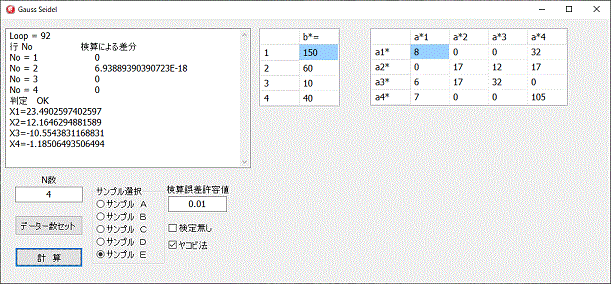 左図は今回のプログラムの実行画面です。
左図は今回のプログラムの実行画面です。
通常はガウス・ザイデル法で計算され、
ヤコビ法のチェックボックスにチェックを入れるとヤコビ法で計算されます。
解法出来るサンプル
ヤコビ法 E
ガウス・ザイデル法 A,B,E
消去法(ピボット操作有り) A,B,C,E
サンプルDは、解法出来ない(答えが無い)値のサンプルです。
プログラムには、前のプログラムを流用したので、結果の検定が残っていますが、解法出来ない値の場合、収束しないので、検定は無意味となっています。
プログラム
unit Main;
interface
uses
Winapi.Windows, Winapi.Messages, System.SysUtils, System.Variants, System.Classes, Vcl.Graphics,
Vcl.Controls, Vcl.Forms, Vcl.Dialogs, Vcl.StdCtrls, Vcl.Buttons, Vcl.Grids, system.UITypes,
Vcl.ExtCtrls;
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
BitBtn1: TBitBtn;
Memo1: TMemo;
StringGrid1: TStringGrid;
StringGrid2: TStringGrid;
LabeledEdit1: TLabeledEdit;
BitBtn2: TBitBtn;
RadioGroup1: TRadioGroup;
LabeledEdit2: TLabeledEdit;
CheckBox1: TCheckBox;
CheckBox2: TCheckBox;
procedure BitBtn1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure BitBtn2Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure RadioGroup1Click(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private 宣言 }
function Jacobi: byte;
function Gauss_Seidel: byte;
procedure GridSet(Sin, Colin: integer); // グリッドサイズ変更
procedure testset;
public
{ Public 宣言 }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
var
Nltest : integer = 4; // テストデーター行列数
// テストデーター
mattestA : array[0..3] of array[0..3] of extended = ((8, 16, 24, 32),
(2, 7, 12, 17),
(6, 17, 32, 59),
(7, 22, 46,105));
mattestB : array[0..3] of array[0..3] of extended = ((8, 16, 24, 32),
(2, 7, 12, 17),
(2, 17, 32, 0),
(7, 0, 0, 105));
mattestC : array[0..3] of array[0..3] of extended = (( 8, 34, 24, 32),
( 2, 7, 32, 0),
(24, 17, 46, 105),
( 7, 0, 0, 32));
mattestD : array[0..3] of array[0..3] of extended = ((8, 16, 24, 0),
(2, 7, 12, 0),
(2, 17, 32, 0),
(7, 0, 0, 105));
mattestE : array[0..3] of array[0..3] of extended = ((8, 0, 0, 32),
(0, 17, 12, 17),
(6, 17, 32, 0),
(7, 0, 0, 105));
btestA : array[0..3] of extended = (160, 70, 198, 291);
btestB : array[0..3] of extended = (150, 60, 10, 40);
Nl : integer; // 行列数
a : array of array of extended;
b : array of extended; // b行列
x : array of extended; // x行列
loop : integer;
allowable_errorr : extended;
epsilon : extended;
// グリッドの設定
procedure TForm1.GridSet(Sin, Colin: integer); // グリッドサイズ変更
var // データー行の数は10迄
H, W, i :integer; // それ以上はスクロールする
begin
inc(Sin);
inc(Colin);
StringGrid1.ColCount := Colin;
StringGrid1.RowCount := Sin;
if Sin <= 11 then begin // ストリンググリッドの大きさ設定 固定行を含め11行又はそれ以下の場合
H := (StringGrid1.DefaultRowHeight + 1) * Sin;
StringGrid2.ScrollBars := ssNone; // スクロールバー表示
end
else begin // 固定行を含め11行より多い場合
H := (StringGrid1.DefaultRowHeight + 1) * (10 + 1);
StringGrid2.ScrollBars := ssVertical; // スクロールバー表示
end;
if Colin <= 11 then begin // ストリンググリッドの大きさ設定 固定行を含め11行又はそれ以下の場合
W := (StringGrid1.DefaultColWidth + 1) * Colin;
StringGrid1.ScrollBars := ssNone; // スクロールバーなし
end
else begin // 固定行を含め11行より多い場合
W := (StringGrid1.DefaultColWidth + 1) * (10 + 1);
StringGrid1.ScrollBars := ssBoth; // スクロールバー表示
end;
StringGrid1.ClientWidth := W;
StringGrid1.ClientHeight := H;
for i := 1 to Sin - 1 do StringGrid1.Cells[0,i] := 'a' + intTostr(i) + '*';
for i := 1 to Sin - 1 do StringGrid1.Cells[i,0] := 'a*' + intTostr(i);
StringGrid2.RowCount := Sin;
StringGrid2.ClientHeight := H + 1;
StringGrid2.ClientWidth := (StringGrid2.DefaultColWidth + 1) * 2;
for i := 1 to Sin - 1 do StringGrid2.Cells[0, i] := intTostr(i);
StringGrid2.Cells[1, 0] := 'b*=';
end;
// ヤコビ法
function TForm1.Jacobi: byte;
var
y : array of extended;
i, j, k, l : integer;
begin
setlength(y, Nl);
loop := 0;
result := 0;
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do x[i] := 0; // 初期値
for k := 0 to Nl * 2000 do begin
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
y[i] := b[i];
for j := 0 to Nl - 1 do
if j <> i then y[i] := y[i] - a[i, j] * x[j];
y[i] := y[i] / a[i, i];
end;
for l := 0 to Nl -1 do
if abs(y[l] - x[l]) > epsilon * (1 + abs(x[l])) then break; // 収束判定
if l = Nl then begin
result := 1;
break;
end;
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do x[i] := y[i];
inc(loop);
end;
end;
// ガウス・ザイデル法による連立方程式の解法
function TForm1.Gauss_Seidel: byte;
var
s : extended;
i, j, iter: integer;
begin
loop := 0;
result := 0;
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do x[i] := 0; // 初期値
for iter := 1 to Nl * 1000 do begin
result := 1;
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
s := b[i];
for j := 0 to i - 1 do s := s - a[i, j] * x[j];
for j := i + 1 to Nl - 1 do s := s - a[i, j] * x[j];
s := s / a[i, i];
if (result = 1) and (abs(x[i] - s ) > epsilon * (1 + abs(s))) then result := 0; // 収束判定
x[i] := s;
end;
inc(loop);
if result = 1 then break; // 収束した場合ブレーク
end;
end;
procedure TForm1.BitBtn1Click(Sender: TObject);
const
sp = ' ';
var
i, j, ch : integer;
maxb, minb, bc : extended;
acmax : array of extended;
acmin : array of extended;
y : array of extended;
LL, spl : string;
sum : extended;
k, n, h : integer;
begin
setlength(a, Nl, Nl);
setlength(b, Nl);
setlength(y, Nl);
setlength(x, Nl);
setlength(acmax, Nl);
setlength(acmin, Nl);
// matAにグリッド1から値読み込み
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do
for j := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
val(StringGrid1.Cells[i + 1,j + 1], a[j,i], ch);
if ch <> 0 then begin
MessageDlg('a' + intTostr(j + 1) + ',' + intTostr(i + 1) + ' の入力値の' + intTostr(ch) + '文字目に誤りが有ります。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
exit;
end;
end;
// bにグリッド2から値読み込み
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
val(StringGrid2.Cells[1, i + 1], b[i], ch);
if ch <> 0 then begin
MessageDlg('b' + intTostr(i + 1) + 'の入力値の' + intTostr(ch) + '文字目に誤りが有ります。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
exit;
end;
end;
// 検算許容誤差
val(labelededit2.Text, allowable_errorr, ch);
if ch <> 0 then begin
MessageDlg('検算誤差許容値の入力値の' + intTostr(ch) + '文字目に誤りが有ります。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
exit;
end;
// 対角0の確認
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
if a[i, i] = 0 then begin
MessageDlg('対角 a' + intTostr(i + 1) + ',' + intTostr(i + 1) + 'の値が0(ゼロ)です。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
exit;
end;
end;
// A行列の最大値最小値検索
for i := 0 to Nl -1 do begin
acmax[i] := 1;
acmin[i] := 1;
if a[i, 0] <> 0 then acmax[i] := abs(a[i, 0]);
if a[i, 0] <> 0 then acmin[i] := abs(a[i, 0]);
for j := 1 to Nl - 1 do begin
if (abs(a[i, j]) > acmax[i]) and (a[i, j] <> 0) then acmax[i] := abs(a[i, j]);
if (abs(a[i, j]) < acmin[i]) and (a[i, j] <> 0) then acmin[i] := abs(a[i, j]);
end;
end;
// B行列とA行列の比最小値と最大値検索
maxb := abs(b[0]) / acmax[0];
minb := abs(b[0]) / acmin[0];
for i := 1 to Nl - 1 do begin
if abs(b[i]) / acmax[i] > maxb then maxb := abs(b[i]) / acmax[i];
if abs(b[i]) / acmin[i] < minb then minb := abs(b[i]) / acmin[i];
end;
// 検算結果の判定値設定
bc := minb;
if (minb = 0) and (maxb > 0) then
if maxb >= 1 then bc := 1 / maxb
else bc := maxb;
if (minb > 0) and (maxb > 0) then bc := minb / maxb;
if (minb = 0) and (maxb = 0) then bc := 1;
if checkbox1.Checked = false then
if bc < epsilon then begin
MessageDlg('bの入力値の値が演算の範囲を超えています。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
memo1.Clear;
exit;
end;
// 検算結果の判定値設定
allowable_errorr := allowable_errorr * sqrt(bc); // 誤差判定値
memo1.Clear;
// 連立方程式の解法 解法できない場合あり
if checkbox2.Checked = true then j := Jacobi
else j := Gauss_Seidel;
memo1.Lines.Append('Loop = ' + inttostr(loop));
// 解法出来なかったら
if j = 0 then begin
MessageDlg('収束しません。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
exit;
end;
// 各行X値代入答えの差分計算
for j := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
sum := 0;
for i := 0 to Nl - 1 do
sum := sum + a[j, i] * x[i]; // 行の値
y[j] := b[j] - sum; // 差分
end;
// 各行の差分値表示
memo1.Lines.Append('行 No 検算による差分');
for k := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
LL := 'No = ' + inttostr(k + 1);
n := 25 - length(LL);
spl := '';
for j := 1 to n do spl := spl + sp;
memo1.Lines.Append(LL + spl + floattostr(y[k]));
end;
// 差分判定
h := 0;
for k := 0 to Nl - 1 do begin
if abs(b[k]) > allowable_errorr then sum := y[k] / b[k]
else sum := y[k];
if abs(sum) > allowable_errorr then inc(h);
end;
if checkbox1.Checked = false then begin
if h = 0 then memo1.Lines.Append('判定 OK')
else memo1.Lines.Append('判定 NG');
if h > 0 then exit;
end;
// xの値表示
for k := 0 to Nl - 1 do
memo1.Lines.Append('X' + inttostr(k + 1) + '=' + floatTostr(x[k]));
end;
// テストデーターの選択設定
procedure TForm1.testset;
var
i, j : integer;
begin
GridSet(Nltest, Nltest);
Nl := Nltest;
for i := 1 to Nltest do
for j := 1 to Nltest do begin
case RadioGroup1.ItemIndex of
0: StringGrid1.Cells[i,j] := floatTostr(mattestA[j-1, i-1]);
1: StringGrid1.Cells[i,j] := floatTostr(mattestB[j-1, i-1]);
2: StringGrid1.Cells[i,j] := floatTostr(mattestC[j-1, i-1]);
3: StringGrid1.Cells[i,j] := floatTostr(mattestD[j-1, i-1]);
4: StringGrid1.Cells[i,j] := floatTostr(mattestE[j-1, i-1]);
end;
end;
for i := 1 to Nltest do begin
case RadioGroup1.ItemIndex of
0: StringGrid2.Cells[1,i] := floatTostr(btestA[i-1]);
1, 2, 3, 4: StringGrid2.Cells[1,i] := floatTostr(btestB[i-1]);
end;
end;
LabeledEdit1.Text := intTostr(Nltest);
memo1.Clear;
end;
// グリッドサイズの変更
procedure TForm1.BitBtn2Click(Sender: TObject);
var
ch : integer;
begin
val(LabeledEdit1.Text, Nl, ch);
if ch <> 0 then begin
MessageDlg('N数の入力値の' + intTostr(ch) + '文字目に誤りが有ります。', mtInformation,[mbOk], 0);
exit;
end;
GridSet(Nl, Nl);
end;
procedure TForm1.RadioGroup1Click(Sender: TObject);
begin
testset;
end;
// 初期値の設定
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
var
a : extended;
begin
testset;
epsilon := 1;
repeat
epsilon := epsilon / 2;
a := 1 - epsilon;
until a = 1;
epsilon := epsilon * 2;
end;
end.
![]() Gauss_Seidel.zip
Gauss_Seidel.zip
三角関数、逆三角関数、その他関数、 連立一次方程式の解法 に戻る