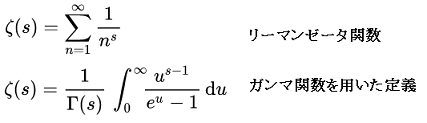
C言語辞典のゼータ関数の場合、sの値がマイナス側になると、誤差が大きくなるので、次の計算を使用することにより、ゼータ関数の計算がプラスとなり、sの値がマイナス側でも精度よく計算が出来るようになります。
但し、ガンマ関数の計算が必要となる為、プログラムが少し長くなります。
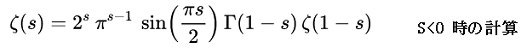
2020/11/28 C言語辞典のゼータ関数を修正した計算マイナス側の計算精度向上の為、マイナス側の計算式追加。
2020/11/22 C言語辞典のゼータ関数を修正した計算の計算精度UPの為の変更
double ->
extended 変更
リーマンゼータ関数
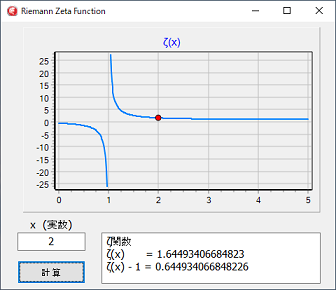
リーマンゼータ関数のζ(s)とζ(s)-1の計算です。
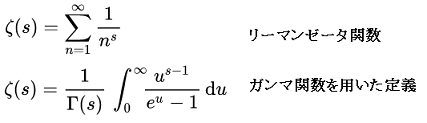
C言語辞典のゼータ関数の場合、sの値がマイナス側になると、誤差が大きくなるので、次の計算を使用することにより、ゼータ関数の計算がプラスとなり、sの値がマイナス側でも精度よく計算が出来るようになります。
但し、ガンマ関数の計算が必要となる為、プログラムが少し長くなります。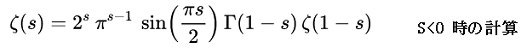

次のプログラムはMathematics Source Library C & ASM にあった
riemann_zeta_function.c をDelphiに変換したものです。
使用されていないルーチンや無駄なルーチンもあるので、他のプログラムに組み込む場合は、後述のプログラムの方が、小さく簡単です。
実行画面は、同じです。
unit main;
interface
uses
Winapi.Windows, Winapi.Messages, System.SysUtils, System.Variants, System.Classes, Vcl.Graphics,
Vcl.Controls, Vcl.Forms, Vcl.Dialogs, system.Math, Vcl.StdCtrls, Vcl.Buttons,
Vcl.ExtCtrls, VclTee.TeeGDIPlus, VCLTee.Series, VCLTee.TeEngine,
VCLTee.TeeProcs, VCLTee.Chart, system.UITypes;
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
Memo1: TMemo;
BitBtn1: TBitBtn;
LabeledEdit1: TLabeledEdit;
Chart1: TChart;
Series1: TLineSeries;
Series2: TLineSeries;
Series3: TPointSeries;
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure BitBtn1Click(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private 宣言 }
public
{ Public 宣言 }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
LDBL_EPSILON : extended;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses dirichlet_eta;
function xRiemann_Zeta_Function(s: extended): extended; forward;
function xRiemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s: extended): extended; forward;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// function Riemann_Zeta_Function(s: double): double;
//
// Description:
// The Riemann zeta function is defined as:
// zeta(s) = Sum (1/k^s),
// summed over k = 1,... where s is a complex number with Re(s) > 1,
// then analytically continued to the rest of the complex plane save for
// a simple pole at s = 1.
// This routine calculates the Riemann zeta function for real s != 1.
// If s = 1, DBL_MAX is returned.
// If zeta(s) > DBL_MAX, then DBL_MAX is returned and
// if zeta(s) < -DBL_MAX, then -DBL_MAX is returned. Note that
// lim zeta(s) = -inf where s->1 from the left and lim zeta(s) = inf
// where s->1 from the right.
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function Riemann_Zeta_Function(s: double): double;
var
zeta: extended;
begin
if s = 1.0 then begin
result := MAXDouble;
exit;
end;
zeta := xRiemann_Zeta_Function(s);
if abs(zeta) < MAXDouble then begin
result := zeta;
exit;
end;
if zeta >= MAXDouble then result := MAXDouble
else result := -MAXDouble;
end;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// function xRiemann_Zeta_Function(s: extended): extended
//
// Description:
// The Riemann zeta function is defined as:
// zeta(s) = Sum (1/k^s),
// summed over k = 1,... where s is a complex number with Re(s) > 1,
// then analytically continued to the rest of the complex plane save for
// a simple pole at s = 1.
// This routine calculates the Riemann zeta function for real s != 1.
// If s = 1, LDBL_MAX is returned.
// lim zeta(s) = -inf where s->1 from the left and lim zeta(s) = inf
// where s->1 from the right.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function xRiemann_Zeta_Function(s: extended): extended;
begin
if s = 1.0 then begin
result := MAXExtended;
exit;
end;
result := xDirichlet_Eta_Function(s) / (1.0 - power(2.0, 1.0 - s));
end;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// function Riemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s: double): double;
//
// Description:
// This routine calculates the Riemann zeta star function defined as
// zeta*(s) = zeta(s) - 1,
// where zeta() is the Riemann zeta function for real s != 1.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function Riemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s: double): double;
var
x: extended;
begin
x := xRiemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s);
if abs(x) < MaxDouble then begin
result := x;
exit;
end
else if x > 0.0 then result :=MAXDouble else result := - MAXDouble;
end;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// function xRiemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s : extended): extended;
//
// Description:
// This routine calculates the Riemannt zeta star function defined as
// zeta*(s) = zeta(s) - 1,
// where zeta() is the Riemann zeta function for real s != 1.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function xRiemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s: extended): extended;
var
two_s: extended;
eta: extended;
temp: extended;
begin
two_s := power(2.0, s - 1.0);
eta := xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(s);
if s = 1.0 then begin
result := MAXDouble;
exit;
end;
if s < 0.0 then begin
two_s := 1.0 / two_s;
result := (eta + two_s) / (1.0 - two_s);
exit;
end;
temp := two_s - 1.0;
result := (two_s * eta + 1.0) / temp;
end;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 計算の実行とグラフ作成
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
procedure TForm1.BitBtn1Click(Sender: TObject);
const
n = 400;
var
zeta: double;
star: double;
s : double;
i : integer;
min, max, dx: double;
begin
val(LabeledEdit1.Text, s, i);
if i <> 0 then begin
MessageDlg('xの値に間違いがあります。', mtInformation,
[mbOk], 0, mbOk);
exit;
end;
zeta := Riemann_Zeta_Function(s);
star := Riemann_Zeta_Star_Function(s);
Memo1.Clear;
Memo1.Lines.Add('ζ関数');
// s = 1の時はMaxDoubleになるので∞を表示
if s <> 1 then begin
Memo1.Lines.Add('ζ(x) = ' + floatTostr(zeta));
Memo1.Lines.Text := Memo1.Lines.Text + 'ζ(x) - 1 = ' + floatTostr(star);
// Memo1.Lines.Add('ζ(x) - 1 = ' + floatTostr(star));
end
else begin
Memo1.Lines.Add('ζ(x) = ∞');
Memo1.Lines.Text := Memo1.Lines.Text + 'ζ(x) - 1 = ∞';
end;
Series1.Clear;
Series2.Clear;
Series3.Clear;
// グラフ表示の演算精度はSingle
if abs(zeta) < MaxSingle then Series3.AddXY(s, zeta);
min := round(s - 2);
max := round(s + 3);
dx := (max - min) / n;
for i := 0 to n do begin
s := i * dx + min;
zeta := Riemann_Zeta_Function(s);
if abs(zeta) < 30 then
if s < 1 then Series1.AddXY(s, zeta)
else Series2.AddXY(s, zeta);
end;
end;
//-------------------------------------------
// extended の Epsilon 設定
//-------------------------------------------
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
var
d, m: extended;
begin
Memo1.Clear;
LDBL_EPSILON := 1;
d := 1;
repeat
LDBL_EPSILON := LDBL_EPSILON / 2;
m := d + LDBL_EPSILON;
until m = d;
LDBL_EPSILON := LDBL_EPSILON * 2;
end;
end.
unit dirichlet_eta; interface function xDirichlet_Eta_Function(s : extended): extended; function xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(s: extended): extended; implementation uses system.math, Gamma_Function, main; //function xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(s: extended): extended; forward; function Alternating_Series_Convergence_Acceleration(s: extended): extended; forward; function Sum_Reverse_Order(s : extended): extended; forward; function Reflection_Coefficient(s: extended): extended; forward; //----------------------------------------------------------------------- // function Dirichlet_Eta_Function(s: extended): extended; // // このルーチンは、実数のEta関数を計算します // eta(s)=(1-2 ^(1-s))zeta(s)、 // ここで、zeta()はリーマンゼータ関数です。s> 1の場合、 // eta(s)= Sum(-1)^(k-1)(1 / k ^ s)、 // ここで、合計は k = 1...eta(1)= ln(2) // // s <1の場合、反射式が使用されることに注意してください // s << 0の場合 eta(s)の傾きは、大きさが大きく、摂動が小さい // 引数は大きな絶対誤差を作成する可能性があります。 //----------------------------------------------------------------------- function xDirichlet_Eta_Function(s : extended): extended; begin if (s >= 64.0) then begin result := 1.0; exit; end; result := 1.0 + xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(s); end; //-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // function xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(s: extended): extended; // このルーチンは、次のように定義されたDirichlet's eta関数を計算します // eta *(s)= eta(s)-1、 // ここで、eta()はディリクレのイータ関数です。// //-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- function xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(s: extended): extended; var reflection_coefficientd: extended; begin if s >= 0.0 then begin if s < 18.0 then result := Alternating_Series_Convergence_Acceleration(s) else result := Sum_Reverse_Order(s); exit; end; // Use the reflection formula reflection_coefficientd := Reflection_Coefficient(s); result := reflection_coefficientd * xDirichlet_Eta_Star_Function(1.0 - s) + (reflection_coefficientd - 1.0); end; //--------------------------------------------------------------------------- // function Reflection_Coefficient(s: extended): extemded; // ディリクレのイータ関数の反射公式は次のとおりです。 // eta(s)= {[2 *(1-2 ^(1-s))/(1-2 ^ s)] *Gamma(1-s) // (2 * pi)^(1-s)* cos((1-s)* pi / 2)} * eta(1-s) // ここで、s <0は負の実数です。 // // このルーチンは係数を返します // [2 *(1-2^(1-s))/(1-2^s)]Gamma(1-s)/(2 * pi)^(1-s)*cos((1-s)* pi/2) // ここで、s <0は負の実数です。 //--------------------------------------------------------------------------- function Reflection_Coefficient(s: extended): extended; var one_s: extended; k : integer; v : extended; c : extended; x, temp : extended; begin one_s := 1.0 - s; k := trunc(one_s / 4.0); v := one_s - 4.0 * k; c := cos(v * pi / 2); if abs(c) < 1.8 * LDBL_EPSILON then begin result := 0.0; exit; end; temp := power(2.0, one_s); x := (1.0 - temp) / (temp - 2.0); x := x + x; x := x * c; x := x * xGamma_Function(one_s); x := x / power(pi, one_s); result := x; end; //----------------------------------------------------------------------------- // function Alternating_Series_Convergence_Acceleration(s: extended): extended; // このルーチンは、s <= 18のEta関数を計算します。 // ゆっくりと収束します。 // Technique: // Given an alternating series: Sum (-1)^k a[k] summmed over k = 0,... // where a[k] > 0 for all k. If there exits a positive function w(x) // defined on [0,1] such that a[k] = I[0,1] x^k w(x) dx (the integral // from 0 to 1 with respect to x of x^k w(x), then // Sum (-1)^k a[k] = Sum (-1)^k I[0,1] x^k w(x) dx // = I[0,1] Sum (-1)^k x^k w(x) dx // = I[0,1] w(x) / (1 + x) dx // // Let S = I[0,1] w(x) / (1 + x) dx. // Given a polynomial P(x) of degree n such that P(-1) != 0, // P(x) = p[0] - p[1] x + p[2] x^2 - ... (-1)^n p[n] x^n, // define S[n] = I[0,1] (P(-1) - P(x)) w(x) / (1+x) dx / P(-1). // Then S[n] = S - I[0,1] P(x) w(x) / (1+x) dx / P(-1) // so, |S[n] - S| <= I[0,1] |P(x)| w(x) / (1+x) dx / |P(x)| // |S[n] - S| <= (M / |P(-1)|) S, where M = max |P(x)|, x in [0,1]. // // After a little algebra, // S[n] = (1/P(-1)) Sum Sum p[j] [(-1)^k a[k]], // where the first sum is over k = 0,...,n-1 and the second sum is over // j = k+1,...,n. // Let d[k] = Sum p[j] summed for j = k+1,...,n for k = n-1, ..., 0, then // S[n] = (1/c[0]) Sum d[k] (-1)^k a[k] summed k = 0,...,n-1. // // The choice for P(x) programmed here is (-1)^n * T*[n](x), where T*[n] // is the shifted Chebyshev polynomial of the first kind of degree n. // With this choice of P(x), // P(x) = Sum {( n / (n+j) ) C(n+j,2j) 4^j (-x)^j}, // where the sum is over j = 0,...,n and C(n+j,2j) = (n+j)!/[(2j)!(n-j)!] // and M = 1, P(-1) >= (1/2) (3 + sqrt(8))^n. //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ function Alternating_Series_Convergence_Acceleration(s: extended): extended; const d: array[0..28] of extended = ( 1.362725501650887306817e+21, 1.362725501650887306816e+21, 1.362725501650887305248e+21, 1.362725501650886896000e+21, 1.362725501650844334208e+21, 1.362725501648488235008e+21, 1.362725501568066715648e+21, 1.362725499718371770368e+21, 1.362725469310199922688e+21, 1.362725096810094788608e+21, 1.362721590926752350208e+21, 1.362695647390018306048e+21, 1.362542007743905005568e+21, 1.361803869444099801088e+21, 1.358896740140251611136e+21, 1.349437033675348770816e+21, 1.323863206542645919744e+21, 1.266218975223368122368e+21, 1.157712186857668739072e+21, 9.872015194258554224640e+20, 7.640581139674368573440e+20, 5.220333434317674905600e+20, 3.061506212814840135680e+20, 1.496014168469232680960e+20, 5.884825485587356057600e+19, 1.781624012587768217600e+19, 3.882102878793367552000e+18, 5.404319552844595200000e+17, 3.602879701896396800000e+16); var term: array[0..27] of extended; sum: extended; k: integer; begin k := 0; while k <= 27 do begin term[k] := d[k + 1] * power(k + 2,-s); inc(k); term[k] := -d[k + 1] * power(k + 2,-s); inc(k) end; sum := term[27]; for k := 26 downto 0 do sum := sum + term[k]; sum := sum / d[0]; result := -sum; end; //------------------------------------------------------------------------- // long double Sum_Reverse_Order(long double s)// // // このルーチンは、s> = 18のEta関数を計算します(power()への呼び出しは28未満) // eta(s)= Sum(-1)^(k-1)(1 / k ^ s)、 // ここで、合計はk = 1、...で合計されます // // Since the series is alternating, the absolute error is less than the // absolute value of the first neglected term. The number of terms which // are summed is determined by calculating successive lower and upper // bounds until the two bounds are equal (within truncation errors). // The final result is then summed starting with the last term and // terminating with the first term, (this is slightly more accurate). //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- function Sum_Reverse_Order(s : extended): extended; var term: array[0..29] of extended; lower_bound: extended; upper_bound: extended; sum: extended; k: integer; begin lower_bound := -power(2.0, -s); term[0] := lower_bound; term[1] := power(3.0 ,-s); upper_bound := term[1] + lower_bound; if lower_bound = upper_bound then begin result := upper_bound; exit; end; k := 4; while k <= 31 do begin term[k-2] := -power(k, -s); lower_bound := upper_bound + term[k - 2]; if lower_bound = upper_bound then break; inc(k); term[k - 2] := power(k, -s); upper_bound := lower_bound + term[ k- 2]; if lower_bound = upper_bound then break; inc(k); end; k := k - 2; sum := term[k]; for k := k - 1 downto 0 do sum := sum + term[k]; result := sum; end; end.
unit Gamma_Function;
interface
function xGamma_Function(x: extended): extended;
implementation
uses system.math;
const
LONG_MAX = 2147483647;
max_long_double_arg: extended = 1755.5;
g = 9.65657815377331589457187;
e = 2.71828182845904523536028747;
exp_g_o_sqrt_2pi = 6.23316569877722552586386e+3;
a: array[0..8] of extended = (
+1.14400529453851095667309e+4,
-3.23988020152318335053598e+4,
+3.50514523505571666566083e+4,
-1.81641309541260702610647e+4,
+4.63232990536666818409138e+3,
-5.36976777703356780555748e+2,
+2.28754473395181007645155e+1,
-2.17925748738865115560082e-1,
+1.08314836272589368860689e-4
);
function xGamma(x: extended): extended; forward;
//=============================================================================
//
// この関数はLanczosの式を使用して実際のGamma(x)を計算します。
// xの範囲は -(max_long_double_arg-1) < x < max_long_double_arg。
// ガンマ関数は複素平面で有理型であり、正でない整数の値
// xaの正の整数または半分の正の整数をテストすると、
// 最大絶対相対誤差は約3.5e-16です。
//
// x > max_long_double_argの場合、lnGamma(x)を使用する必要があります。
// x < 0 の場合、ln(Gamma(x)) は複素数になる可能性があることに注意してください。
//
// 戻り値
// xが正で、max_long_double_argより小さい場合、Gamma(x)
// が返され、x > max_long_double_argの場合、maxextendedが返されます。
// xが正でない整数の場合、maxextendedが
// 返されます(Gamma(x)は値の両側で符号を変更することに注意してください)。
// xが非正の非整数の場合でx>-(max_long_double_arg + 1)の場合
// Gamma(x)が返されます。それ以外の場合は0.0が返されます
//
//=============================================================================
function xGamma_Function(x: extended): extended;
var
sin_x: extended;
rg: extended;
ix: int64;
begin
if x > 0 then
if x <= max_long_double_arg then begin
result := xGamma(x);
exit;
end
else begin
result := maxextended;
exit;
end;
if x > -LONG_MAX then begin
ix := round(x);
if x = ix then begin
result := maxextended;
exit;
end;
end;
sin_x := sin(pi * x);
if sin_x = 0 then begin
result := maxextended;
exit;
end;
if x < - max_long_double_arg - 1 then begin
result := 0;
exit;
end;
rg := xGamma(1 - x) * sin_x / pi;
if rg <> 0 then result := 1 / rg
else result := maxextended;
end;
//=============================================================================
//
// この関数は倍数公式を使用してGamma(two_x)を返します。
//
//=============================================================================
function Duplication_Formula(two_x: extended): extended;
var
x: extended;
g: extended;
n: integer;
begin
x := 0.5 * two_x;
n := round(two_x) - 1;
g := power(2.0, two_x - 1.0 - n);
g := g * power(2, n);
g := g / sqrt(pi);
g := g * xGamma_Function(x);
g := g * xGamma_Function(x + 0.5);
result := g;
end;
//=============================================================================
//
// この関数はLanczosの式を使用して実際のGamma(x)を計算します。
// x、ここで0<x<=900。900<x<1755.5の場合、倍数公式を使用します。
// 関数power()。結果の相対誤差は約10^-16です。x = 0付近を除きます。
// x>1755.5の場合、lnGamma(x)を計算する必要があります。
// xが正で1755.5未満の場合、Gamma(x)が返され、
// x>1755.5の場合、maxextendedが返されます。
//
//=============================================================================
function xGamma(x: extended): extended;
var
xx: extended;
temp: extended;
n, i: integer;
xx2 : extended;
begin
if x < 1 then xx := x + 1 else xx := x;
n := sizeof(a) div sizeof(extended);
if x > max_long_double_arg then begin
result := maxextended;
exit;
end;
if x > 900 then begin
result := Duplication_Formula(x);
exit;
end;
temp := 0;
for i := n - 1 downto 0 do temp := temp + a[i] / (xx + i);
temp := temp + 1;
xx2 := (xx - 0.5) / 2;
temp := temp * (power((g + xx - 0.5) / e, xx2) / exp_g_o_sqrt_2pi );
temp := temp * power((g + xx - 0.5) / e, xx2); // X64 オーバーフロー対策
if x < 1 then result := temp / x
else result := temp;
end;
end.
次のプログラムは、C言語辞典にあるRiemannのゼータ関数を修正したものです。
xの値が-5より小さくなると、誤差が大きくなっていきます。
2020/11/28 C言語辞典のゼータ関数を修正した計算マイナス側の計算精度向上の為、マイナス側の計算式追加。
2020/11/22 計算精度UPの為の変更
double -> extended 変更 x がマイナスの時の精度向上
unit Main;
interface
uses
Winapi.Windows, Winapi.Messages, System.SysUtils, System.Variants, System.Classes, Vcl.Graphics,
Vcl.Controls, Vcl.Forms, Vcl.Dialogs, Vcl.StdCtrls, Vcl.Buttons, Vcl.ExtCtrls, VclTee.TeeGDIPlus,
VCLTee.Series, VCLTee.TeEngine, VCLTee.TeeProcs, VCLTee.Chart;
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
Memo1: TMemo;
BitBtn1: TBitBtn;
LabeledEdit1: TLabeledEdit;
Chart1: TChart;
Series1: TLineSeries;
Series2: TPointSeries;
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure BitBtn1Click(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private 宣言 }
public
{ Public 宣言 }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
uses system.Math;
var
GrphF: boolean;
function Gamma(x: Extended): Extended; // ガンマ関数
const
//ベルヌーイ数B(2)、B(4)、B(6)、...、B(16)
B : array[1..8] of Extended = ( 1.0 / 6, // B(2)
-1.0 / 30,
1.0 / 42,
-1.0 / 30,
5.0 / 66,
-691.0 / 2730,
7.0 / 6,
-3617.0 / 510); // B(16)
m: integer = sizeof(B) div sizeof(Extended);
var
i : integer;
sum : Extended;
xx, v : Extended;
xj : Extended;
lng : Extended;
ln_sqrt_2pi: Extended;
begin
ln_sqrt_2pi := ln(sqrt(2 * pi)); // = ln(2 * pi) / 2;
sum := 0;
v := 1;
while x < m do begin
v := v * x;
x := x + 1;
end;
xx := x * x;
xj := x;
lng := ln_sqrt_2pi - x + (x - 0.5) * ln(x) - ln(v);
for i := 1 to m do begin
sum := sum + B[i] / (i * 2 * (2 * i - 1)) / xj;
xj := xj * xx;
end;
result := exp(sum + lng);
end;
function Riemann_Zeta_Function(x: Extended): Extended;
const
coef: array[0..19] of Extended = (
8.333333333333333333333333333e-2, // 1/12
-1.388888888888888888888888889e-3, // -1/720
3.306878306878306878306878307e-5, // 1/30240
-8.267195767195767195767195767e-7, // -1/1209600
2.087675698786809897921009032e-8, // 1/47900160
-5.284190138687493184847682202e-10,
1.338253653068467883282698098e-11,
-3.389680296322582866830195391e-13,
8.586062056277844564135905450e-15,
-2.174868698558061873041516424e-16,
5.509002828360229515202652609e-18,
-1.395446468581252334070768626e-19,
3.534707039629467471693229977e-21,
-8.953517427037546850402611251e-23,
2.267952452337683060310950058e-24,
-5.744790668872202445263829503e-26,
1.455172475614864901866244572e-27,
-3.685994940665310178130050728e-29,
9.336734257095044668660153106e-31,
-2.365022415700629886484029550e-32
);
var
i, N : integer;
powNx, w, z, zprev: Extended;
begin
if x = 1 then begin
result := infinity;
exit;
end;
z := 1;
zprev := z;
N := 8;
for i := 2 to N - 1 do begin
zprev := z;
z := z + power(i, -x);
if z = zprev then begin
result := z;
exit;
end;
end;
powNx := power(N, x);
w := x / (N * powNx);
z := z + 0.5 / powNx + N / ((x - 1) * powNx) + coef[0] * w;
i := 1;
while (i < 20) and (z <> zprev) do begin
w := w * (x + 2 * i - 1) * (x + 2 * i) / (N * N);
zprev := z;
z := z + coef[i] * w;
inc(i);
end;
result := z;
end;
function RiemannFunction(s: Extended): Extended;
var
term : Extended;
ints : integer;
def : Extended;
begin
ints := trunc(s);
def := s - ints;
if (s <= -2) and (def = 0) and (ints mod 2 = 0) then
result := 0
else
if s < -1 then begin
term := power(2, s) * power(pi, s - 1) * sin(pi * s / 2);
result := term * Riemann_Zeta_Function(1 - s) * Gamma(1 - s);
end
else
result := Riemann_Zeta_Function(s);
end;
procedure TForm1.BitBtn1Click(Sender: TObject);
const
n = 400;
var
zeta, s, star: Extended;
ch, i : integer;
min, max, dx: Extended;
gyi : Extended;
begin
val(labeledEdit1.Text, s, ch);
if ch <> 0 then begin
application.MessageBox('入力値に間違いがあります','注意',0);
exit;
end;
memo1.Clear;
GrphF := False;
zeta := riemannFunction(s);
star := zeta - 1;
if s <> 1 then begin
Memo1.Lines.Add('ζ(x) = ' + floatTostr(zeta));
Memo1.Lines.Text := Memo1.Lines.Text + 'ζ(x) - 1 = ' + floatTostr(star);
end
else begin
Memo1.Lines.Add('ζ(x) = ∞');
Memo1.Lines.Text := Memo1.Lines.Text + 'ζ(x) - 1 = ∞';
end;
Series1.Clear;
Series2.Clear;
application.ProcessMessages;
gyi := 30;
if s < -3 then gyi := MaxDouble / 2;
if abs(zeta) < gyi then Series2.AddXY(s, zeta);
GrphF := True;
min := round(s - 2);
max := round(s + 3);
dx := (max - min) / n;
for i := 0 to n do begin
s := i * dx + min;
zeta := riemannFunction(s);
if abs(zeta) <= gyi then
Series1.AddXY(s, zeta,'', $FF8000)
else begin
if zeta > gyi then zeta := gyi;
if zeta < -gyi then zeta := -gyi;
if zeta > 0 then
Series1.AddXY(s, gyi,'', clbtnface)
else
Series1.AddXY(s, -gyi,'', clbtnface);
end;
end;
end;
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
memo1.Clear;
end;
end.